Model-Based Design
Model-Based Design (MBD) in control systems is a systematic approach that utilizes mathematical models to design, simulate, and validate control algorithms and systems.
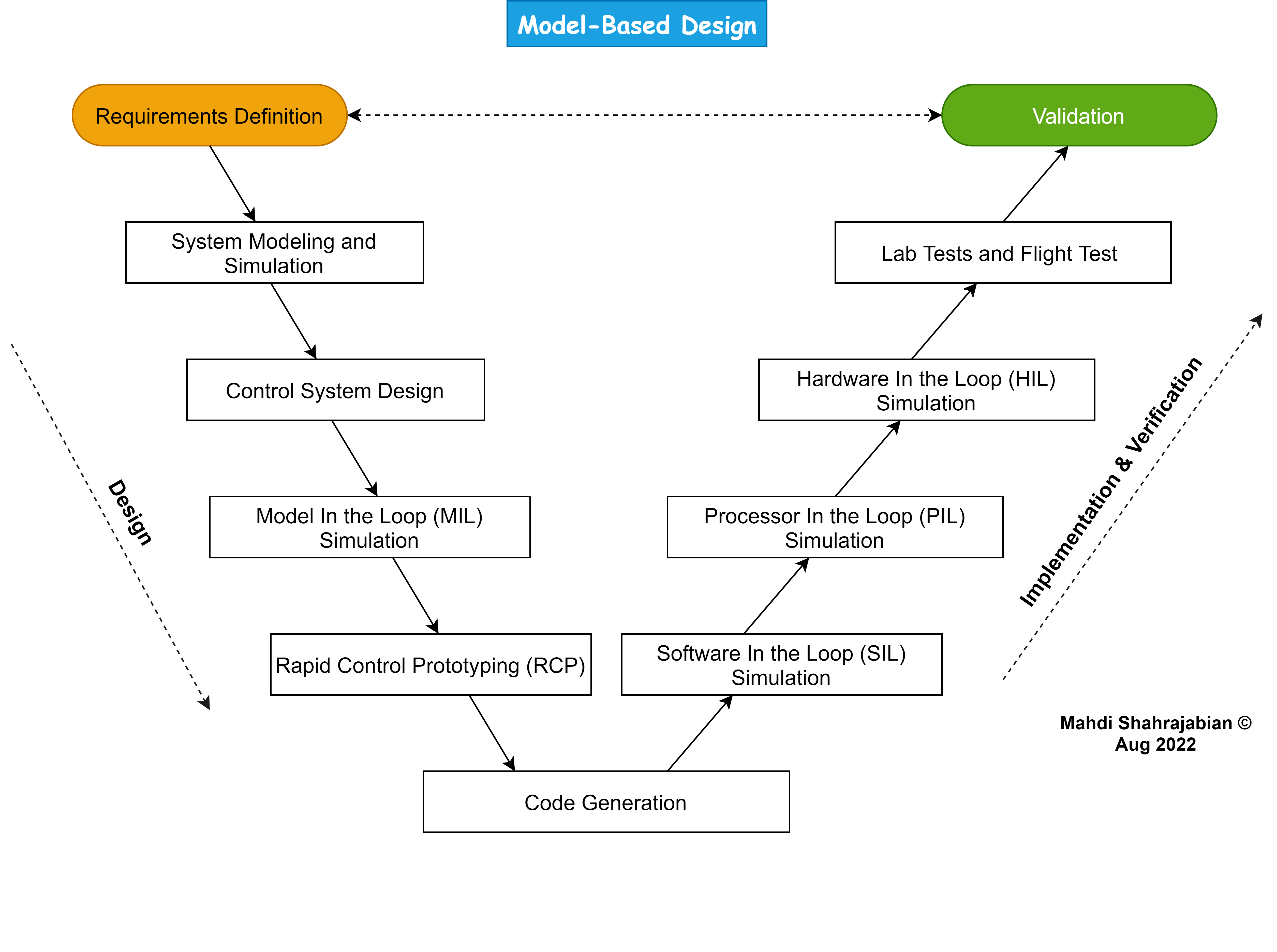
The process begins with defining requirements and creating a mathematical representation of the system, enabling engineers to analyze its dynamics effectively. Model-based control algorithms are then developed and tested through model-in-the-loop simulations, often using tools like MATLAB/Simulink, to evaluate critical performance metrics such as stability and response time. Once validated, automatic code generation facilitates the implementation of these algorithms on hardware. This is followed by Software-in-the-Loop (SIL), Processor-in-the-Loop (PIL), and Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) testing to ensure real-time performance. While PIL and HIL are sometimes used interchangeably, HIL is more general and can involve integrating various hardware components, including sensors and actuators, beyond just the processor.
This iterative process allows for continuous refinement of both the model and control strategies, ultimately leading to improved accuracy, reduced development time, and cost efficiency. MBD is widely applied in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and robotics, enhancing collaboration among engineers and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
The diagram below illustrates a comprehensive V-diagram representing the Model-Based Design (MBD) process for control systems, specifically tailored for aerial vehicles.