MSc Project
Safe Intelligent Control of Air Taxis
Fault-Tolerant Adaptive Intelligent Control of an Autonomous Multi-rotor eVTOL Air Taxi
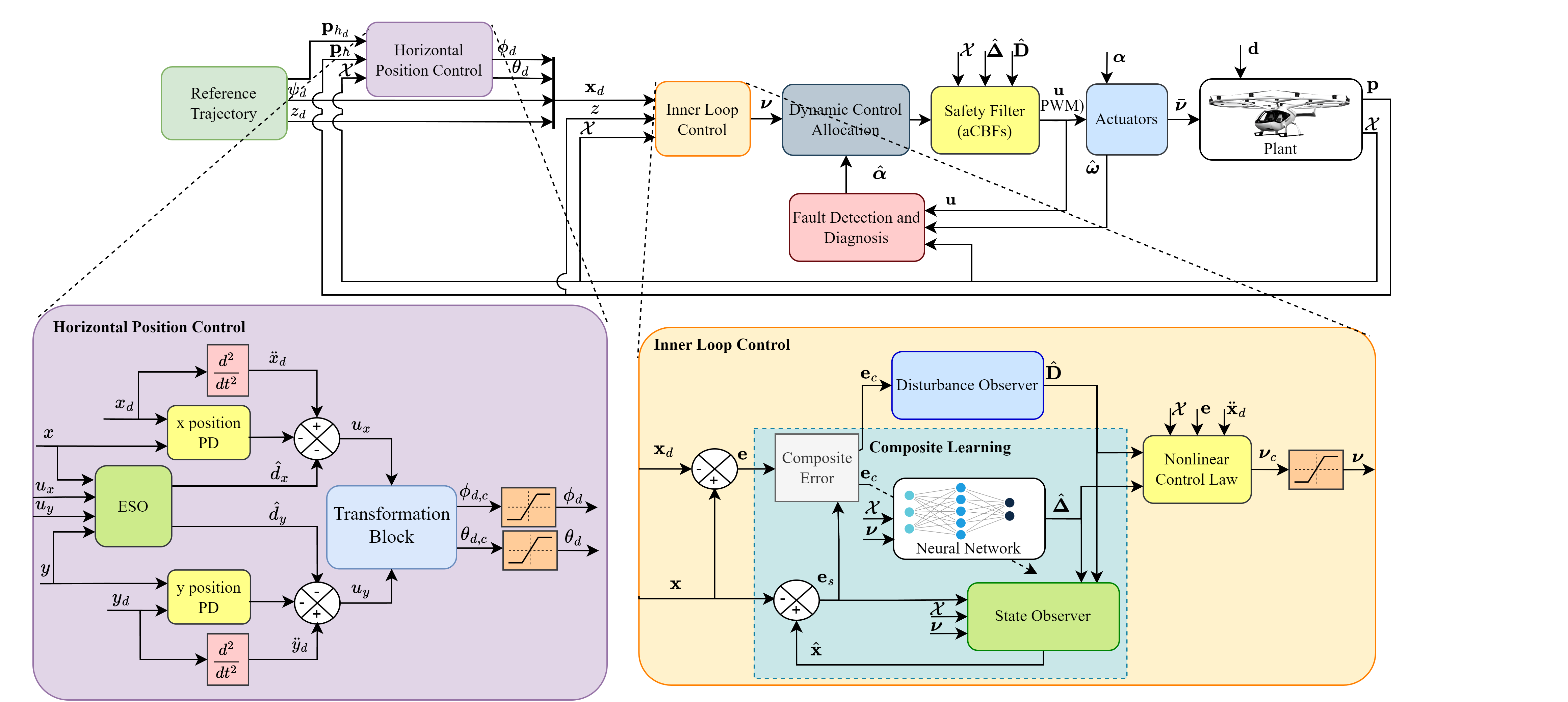
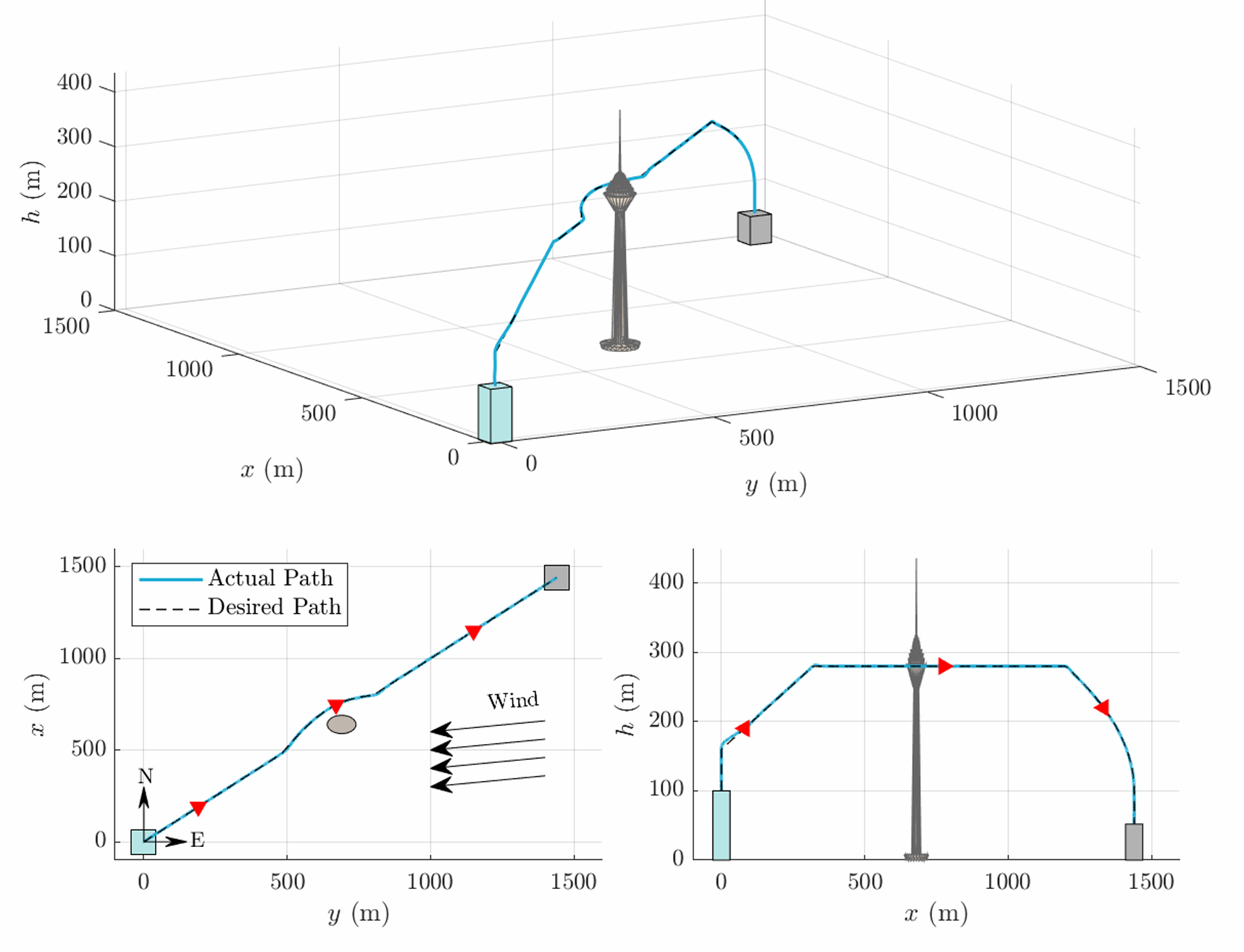
The rapid growth of urban populations has intensified transportation challenges such as congestion, pollution, and limited mobility, driving demand for autonomous electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) air taxis. Developing autonomous systems requires safety guarantees and robust control systems capable of handling uncertainties, disturbances, and actuator faults. This research introduces an Intelligent control framework for a multirotor eVTOL in Urban Air Mobility applications. The inner-loop attitude/altitude tracking employs a Composite Adaptive Neural Control with Disturbance Observer (CANCDO), combining Lyapunov-based neural network adaptation to compensate for uncertainties and a disturbance observer to estimate the upper bound of disturbances and compensate for estimation errors. The framework simultaneously trains the neural network and disturbance observer online based on a composite error that consists of both tracking error and the state estimation error from an adaptive observer. The outer-loop horizontal position control uses a PD controller enhanced with an Extended State Observer (ESO) for precise trajectory tracking. For fault tolerance, we propose a two-stage Fault Detection and Diagnosis (FDD) scheme that estimates actuator effectiveness coefficients in real time, paired with dynamic control allocation to optimally distribute virtual control efforts during failures. Additionally, adaptive Control Barrier Functions (aCBFs) enforce safety constraints on position and velocity by incorporating real-time uncertainty estimates from CANCDO, ensuring safe operation despite model discrepancies. The framework is validated on a high-fidelity multirotor air taxi model, demonstrating a 36\% reduction in trajectory tracking RMSE compared to conventional PID controllers—achieving a final Relative RMSE of 0.34\% under simultaneous faults (partial/complete motor failures) and severe wind disturbances exceeding 20 m/s. Therefore, by unifying adaptive intelligent control, fault diagnosis, and safety guarantees, this work advances assured autonomy for multirotor eVTOLs in urban air mobility.
Contributions:
- Developed a high-fidelity simulation framework incorporating gyroscopic effects, rotor and body aerodynamic effects, ground effect, and wind disturbances to evaluate the proposed methods under realistic urban flight scenarios.
- Proposed a Composite-Learning-Based Adaptive Neural Control with Disturbance Observer (CANCDO) approach considering input constraints for the second-order systems (multirotors) to improve the quality of online uncertainty estimation and capable of robust trajectory tracking under system uncertainties, external disturbances.
- Developed a dynamic control allocation algorithm based on a novel two-stage Fault Detection and Diagnosis (FDD) framework, combining AEKF and OS-ELM approaches to handle simultaneous actuator faults.
- Developed adaptive CBFs as safety filter for enforcing safety constraints on critical states and guaranteeing operation within safe flight envelopes.
- Compensating for the uncertainty caused by the variability of the thrust and drag torque coefficients in the system model and considering them as constant in the control allocation matrix by the proposed CANCDO approach
The overal architecture of the proposed control system is shown below: